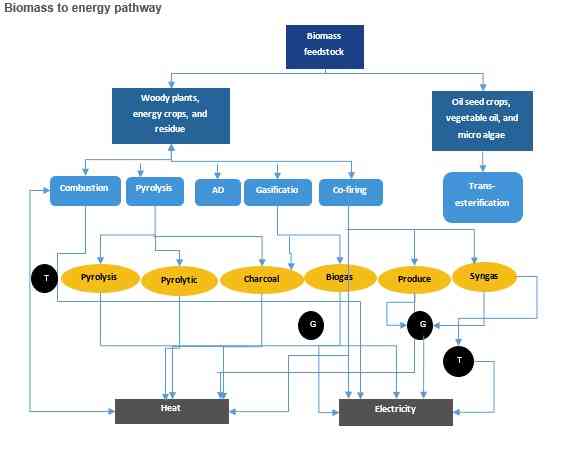
For an energy starved world, biomass energy generation is a boon in disguise. It takes the by-products from various sources like industrial waste, agricultural residue, woody plants, algae, timber, and sugarcane – and turns it into energy. Energy is generated from waste through simple processes like incineration of waste in an uncontrolled environment, and goes up to use of controlled environment for combustion of waste. The technologies used to convert wastes range from energy generated in the form of electricity or heat; or conversion of waste into combustible biogas and liquid biofuel.
Biomass – Future Prospects
Industry experts at Technavio expect the global biomass power generation market to reach 111.1 GW by the year 2019.
Top Five Emerging Biomass Technologies
1) Direct combustion
The simplest way of generating energy from biomass – direct combustion makes use of boilers to burn biomass and produce high-pressure steam. In this case the turbine rotates using steam and thereby produces electricity. Usually biomass power plants employ direct combustion to produce electricity. Even the steam generated in the process is captured to heat water and buildings leading to what is commonly known as co-generation facilities. Co-generation helps in boosting the results generated from direct combustion systems and thereby improve the overall thermal efficiencies.
2) Gasification
Due to technological innovations, biomass can now be generated through gasification as well. The process involves heating of the solid biomass at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. This is done to produce fuel gas which is natural gas upto a concentration of 50%. Fuel gas can be used to drive combined cycle systems to generate electricity. Gasification is twice as efficient as burning biomass directly and results in fewer particulate matter emission and greenhouse gases. This process can also be combined with fuel cell systems, which convert hydrogen gas to electricity and heat.
3) Co-firing
Co-firing is a process which involves burning of biomass along with coal in traditional power plant boilers. One of the most economical ways to produce electricity from biomass, the co-firing system is being used to reduce coal consumptions, nitrogen oxide, and Sulphur dioxide emissions. The process also allows biomass to be easily converted to electricity at a higher thermal efficiency ranging from 33% to 37%.
4) Pyrolysis
A part of gasification systems, pyrolysis is a process which involves partial combustion at a temperature of 842F-1112F. This results in the formation of a liquid bio-oil as well as gaseous and solid products. The pyrolysis oil produced in this process can be used as a fuel in electricity production, and the remaining solid is a charcoal-like residue known as char.
The pyrolysis oil can be used as a fuel to produce electricity, and the remaining solid is a charcoal-like residue known as char. The bio-oil can then be burned like petroleum to generate electricity while the char can be used for heating.
5) Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a process which transforms biomass feedstock with a relatively high moisture content into biogas. The process relies on certain kinds of bacteria to break down organic material in the absence of oxygen and produce biogas as a waste product. This is a naturally occurring procedure and can be harnessed to treat organic material such as energy crops, residues, and wastes from industrial and agricultural processes and municipal waste streams. This gas is collected and used to heat buildings, run engines, and generate electricity.
Energy from biomass is an important topic in the present context of things. Technavio has compiled a wide selection of market research reports that deal with this very important, and lucrative, speciality. Check them out here.